Industries
Emulsion Manufacturing: How to Make and Use Asphalt Emulsions
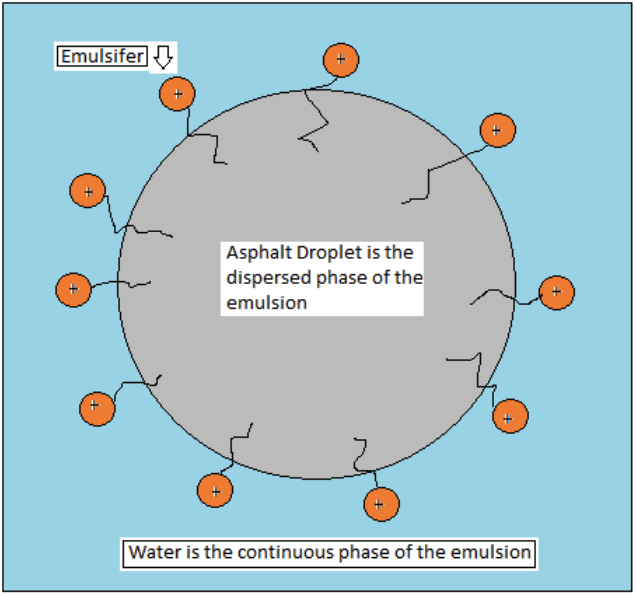
Asphalt emulsions are a type of liquid mixture that consists of asphalt binder, water, and an emulsifying agent. Asphalt binder is a sticky substance that is derived from crude oil and used for paving, roofing, and other applications. Water is a solvent that helps to dilute and disperse the asphalt binder. An emulsifying agent is a chemical that helps to stabilize the mixture and prevent the asphalt binder and water from separating.
The main reason why we make asphalt emulsions is to lower the temperature required for handling and applying the asphalt binder. This reduces the energy consumption, environmental impact, and safety hazards associated with hot asphalt products. Another reason why we make asphalt emulsions is to improve the ability of the asphalt binder to coat damp aggregates, which are the materials that form the base or surface of pavements.
In this article, we will explain how emulsion manufacturing works, what are the ingredients and equipment involved, and what are the benefits of using asphalt emulsions for various applications.
Ingredients of Asphalt Emulsions
The three basic ingredients of asphalt emulsions are:
- Asphalt binder: This is the main component that provides the strength, durability, and flexibility of the asphalt product. The properties of the asphalt binder must be analyzed and tested before use, because not all types of asphalt binder are suitable for emulsion manufacturing. Some factors that affect the suitability of the asphalt binder are the source, the modification, and the compatibility with the emulsifying agent.
- Water: This is the component that dilutes and disperses the asphalt binder into fine droplets. The composition and properties of the water are also very important for emulsion manufacturing. The water must have a certain pH level, be free of contaminants, and be either hard or soft depending on the type of emulsion.
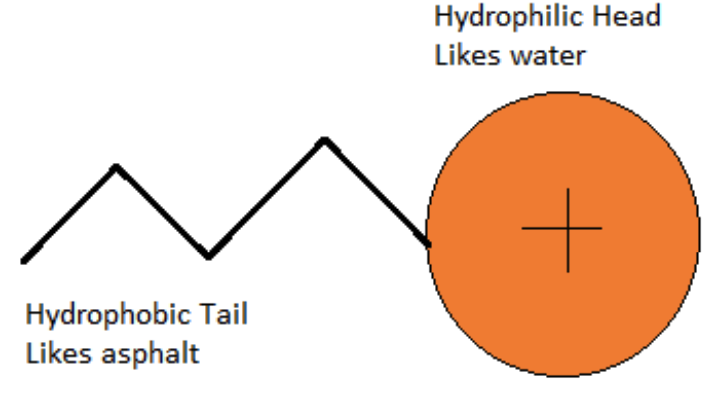
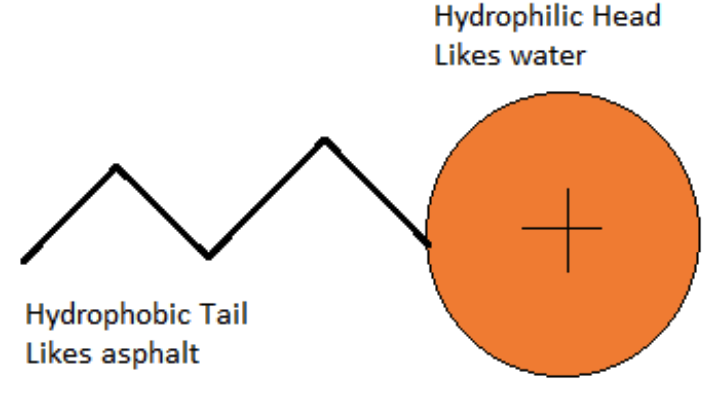
- Emulsifying agent: This is the component that stabilizes the mixture and prevents the asphalt binder and water from separating. The emulsifying agent also determines the charge, the setting time, and the stability of the asphalt droplets. The emulsifying agent can be either cationic or anionic, meaning that it gives a positive or negative charge to the asphalt droplets.
Other ingredients that can be added to asphalt emulsions are:
- Polymers: These are large molecules that can modify the rheology, stability, and performance of asphalt emulsions. Polymers can add elasticity and/or strength to the asphalt binder, making it more resistant to cracking, rutting, and aging.
- Solvents: These are substances that can soften the asphalt binder, improve its adhesion to aggregates during mixing, and slow down its curing time. Solvents can also help to adjust the viscosity and density of asphalt emulsions.
- pH modifying agents: These are substances that can adjust the pH level of asphalt emulsions when the emulsifying agent does not meet the requirement. The pH level affects the stability, reactivity, and breaking behavior of asphalt emulsions.
Equipment for Emulsion Manufacturing
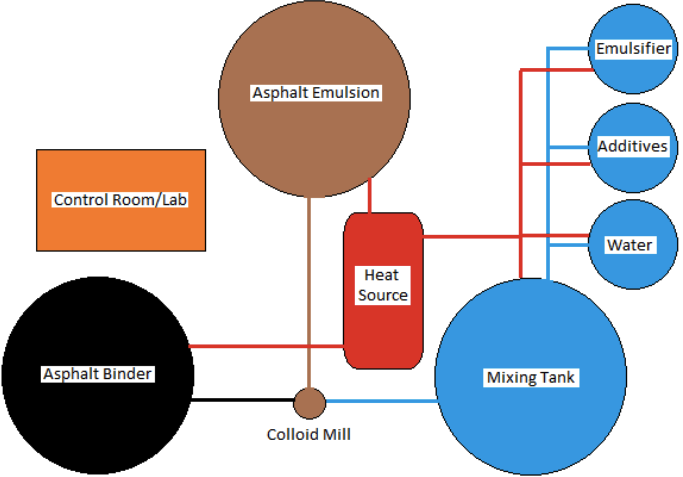
The manufacturing of asphalt emulsions requires specialized equipment that provides the mechanical force needed to shear the asphalt binder into microscopic droplets that then disperse into the water phase. The main equipment used for emulsion manufacturing is:
- Colloid mill: This is a device that consists of a rotor and a stator that mesh closely together and create a narrow gap through which the asphalt binder and water mixture passes. The rotor rotates while the stator remains stationary, creating a high shear rate and energy input that breaks up the asphalt binder into fine droplets. The gap between the rotor and stator determines the particle size of the asphalt droplets produced.
- Asphalt binder storage: This is a tank that stores the asphalt binder at a controlled temperature and prevents it from solidifying or degrading.
- Emulsion storage: This is a tank that stores the finished asphalt emulsion at a controlled temperature and prevents it from separating or spoiling.
- Water storage: This is a tank that stores the water at a controlled temperature and prevents it from freezing or evaporating.
- Mixing tank: This is a tank that mixes the asphalt binder, water, and emulsifying agent in a specific ratio before sending them to the colloid mill.
- Heat source: This is a device that provides heat to maintain or adjust the temperature of various components in emulsion manufacturing.
- Additive storage: This is a tank or container that stores other ingredients such as polymers, solvents, or pH modifying agents that can be added to asphalt emulsions.
- Control room / Laboratory: This is a place where all equipment can be operated and monitored from a single point. It also includes a laboratory where mix designs and quality control tests can be performed on asphalt emulsions.
- Pumps: These are devices that transfer the fluids between different tanks and equipment in emulsion manufacturing.
Benefits of Asphalt Emulsions
Asphalt emulsions offer many benefits for various applications in different industries. Some of the benefits are:
- Lower energy consumption: Asphalt emulsions can be manufactured and applied at lower temperatures than conventional asphalt products, reducing the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating and cooling processes.
- Improved safety: Asphalt emulsions can reduce the risk of fire, explosion, or inhalation hazards associated with hot asphalt products, improving the safety of workers and the environment.
- Enhanced performance: Asphalt emulsions can improve the performance of asphalt products by increasing their adhesion, durability, flexibility, and resistance to water damage, cracking, rutting, and aging.
- Versatility: Asphalt emulsions can be formulated to meet specific requirements for different applications, such as paving, roofing, coating, sealing, or recycling.
- Cost-effectiveness: Asphalt emulsions can reduce the cost of asphalt products by using less material, extending their service life, and simplifying their transportation and storage.
Conclusion
Emulsion manufacturing is a process that involves mixing asphalt binder, water, and an emulsifying agent to create a liquid mixture that consists of fine droplets of asphalt dispersed in water. Emulsion manufacturing requires specialized equipment that provides the mechanical force needed to shear the asphalt binder into microscopic droplets. Emulsion manufacturing also requires careful selection and testing of the ingredients and equipment involved. Emulsion manufacturing offers many benefits for various applications in different industries by lowering energy consumption, improving safety, enhancing performance, increasing versatility, and reducing cost.
If you want to learn more about emulsion manufacturing and its applications, please contact us today.
Industries
Downloads
- Railway Track Road Stabilization
- Mining Application Protocols: Topical and “Mini Stabilization” Techniques
- Asphalt Emulsion Manufacturing
- TopicalDeep Stabilization Application Protocols
- Earthbind® Safety Data Sheet
- Earthbind® Stabilizer Product Information Packet
- Earthbind® MSDS
- QAS Registration Certificate